Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
He, X.*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Okajima, Hajime*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Goto, Hirotada*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Structure, 1310, p.138271_1 - 138271_8, 2024/08
High-pressure responses of the O-D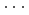 F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)
F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)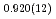 F
F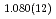 and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm
and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm . The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm
. The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
Watanabe, Teppei*; Sekine, Yurina; Ikeda-Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Macromolecules, 56(16), p.6217 - 6221, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.7(Polymer Science)To investigate the ability of hydrogels to separate hydrogen isotopes in water, we analyzed the Raman spectra of poly-N,N-dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogels containing deuterated water during dehydration. The results show a significant fractionation of hydrogen isotopes during dehydration. The D molar ratio of the hydrogel increases from 0.056 to  0.2 during dehydration from 90.5 wt% to 5 wt% in water content. Deuterated water preferentially forms hydrogen bonds with hydrophilic groups of the polymer in hydrogels because of the difference in strengths of hydrogen bonds between protium and deuterium. As a result, normal water preferentially evaporates in the initial stage of dehydration, leaving deuterated water in the drying hydrogel. The results suggest that hydrogels are an efficient material for isotope fractionation with evaporation.
0.2 during dehydration from 90.5 wt% to 5 wt% in water content. Deuterated water preferentially forms hydrogen bonds with hydrophilic groups of the polymer in hydrogels because of the difference in strengths of hydrogen bonds between protium and deuterium. As a result, normal water preferentially evaporates in the initial stage of dehydration, leaving deuterated water in the drying hydrogel. The results suggest that hydrogels are an efficient material for isotope fractionation with evaporation.
Terasawa, Yukana*; Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Sota*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; Asahi, Toru*
Acta Crystallographica Section E; Crystallographic Communications (Internet), 78(3), p.306 - 312, 2022/03
Yano, Yoshio*; Ono, Toshikazu*; Ohara, Takashi; Hisaeda, Yoshio*
Chemistry; A European Journal, 27(71), p.17802 - 17807, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.82(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nakano, Satoshi*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Fujihisa, Hiroshi*; Yamawaki, Hiroshi*; Goto, Yoshito*; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(5), p.3065 - 3073, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:74.02(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)X-ray and neutron diffraction analyses of ammonia borane were conducted at ambient and high pressures. The H-H distance in dihydrogen bonds was shorter than twice the van der Waals radius (2.4  ). The half of the dihydrogen bonds were broken on phase transition from AP to the first high pressure phase (HP1) at approximately 1.2 GPa as revealed by an increase in the H-H distances. On further pressure increase, all of the H-H distances became shorter than 2.4
). The half of the dihydrogen bonds were broken on phase transition from AP to the first high pressure phase (HP1) at approximately 1.2 GPa as revealed by an increase in the H-H distances. On further pressure increase, all of the H-H distances became shorter than 2.4  again, implying the pressure-induced reformation of the dihydrogen bonds. Furthermore, the HP1 transformed to the second one with the structure of
again, implying the pressure-induced reformation of the dihydrogen bonds. Furthermore, the HP1 transformed to the second one with the structure of 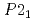 (Z = 2) at about 11 GPa. In this phase transition, the inclination of the molecule axis became larger and the number of types of dihydrogen bonds increased from 6 to 11. Just before the third transition at 18.9 GPa, the shortest dihydrogen bond decreased to 1.65
(Z = 2) at about 11 GPa. In this phase transition, the inclination of the molecule axis became larger and the number of types of dihydrogen bonds increased from 6 to 11. Just before the third transition at 18.9 GPa, the shortest dihydrogen bond decreased to 1.65  . The present study experimentally first confirmed the breakage and reformation of the dihydrogen bonds by the structural change under pressure.
. The present study experimentally first confirmed the breakage and reformation of the dihydrogen bonds by the structural change under pressure.
Tachikawa, Masanori*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 127(34), p.11908 - 11909, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:84 Percentile:84.85(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Isotope effect of hydrogen can sometimes subtlely change the strength of hydrogen bonds. From a detail analysis of positively and negatively charged water clusters by ab initio path integral molecular dynamics, we have found that oxygen-oxygen bonds shortens in positive ions while lengthens in negative ions as a result of deuterization. The former is ascribed to the anharmonicity of the OH bond, the latter is ascribed to the resonance of the O-H-O bond.




 BeH
BeH
Hayashi, Aiko*; Shiga, Motoyuki; Tachikawa, Masanori*
Chemical Physics Letters, 410(1-3), p.54 - 58, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:33.01(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrogen bond is conventionally a bonding between hydrogen and an atom with high electronegativity such as fluorine, oxygen or nitrogen. A dihydrogen bond is an exceptional case, which is an attractive force between positively and negatively charged hydrogen atoms. In this report, some characters of the dihydrogen bond is studied in detail for the molecular cluster BeH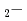 NH
NH
 using ab initio molecular dynamics simulation.
using ab initio molecular dynamics simulation.
Niimura, Nobuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki; Kurihara, Kazuo; Maeda, Mitsuru
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics, 40(3), p.351 - 369, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:25.29(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Neutron diffraction provides an experimental method of directly locating hydrogen atoms in proteins. High resolution neutron diffractometers dedicated to biological macromolecules (BIX-type diffractometer) have been constructed at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and they have been used in the 1.5 AA -resolution crystal structure analyses of several proteins.
Niimura, Nobuo; Chatake, Toshiyuki; Ostermann, A.; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro
Zeitschrift f r Kristallographie, 218(2), p.96 - 107, 2003/03
r Kristallographie, 218(2), p.96 - 107, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Ishida, Hisashi
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 19(5), p.839 - 851, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:26.31(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Satoru; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*
JNC TN8400 2001-005, 41 Pages, 2001/04
A correlation between molecular structure and a vibrational spectrum of interlayer water in Na-smectite was investigated by means of Molecular Dymamics (MDs) simulations. Detailed comparison of simulation results with IR spectroscopic observations for the water-smectite system indicated good agreement. Internal vibrational spectra of water were obtained by the Fourier transformation of velocty auto-correlation function of hydrogen atom. A stretching vibrational spectrum of interlayer water consisted of a broad band with a peak top around 3400cm and a sharp peak around 3650 to 3700cm
and a sharp peak around 3650 to 3700cm . The fomer broad band was assigned to O-H vibrations between water molecules as bulk water, while the latter band was attributed to O-H ones oriented to siloxane surface through hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bond distance, determined as the shortest O-O distance by the radial distribution function (RDF), revealed that hydrogen bond distance between water and siloxane surface (O
. The fomer broad band was assigned to O-H vibrations between water molecules as bulk water, while the latter band was attributed to O-H ones oriented to siloxane surface through hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bond distance, determined as the shortest O-O distance by the radial distribution function (RDF), revealed that hydrogen bond distance between water and siloxane surface (O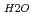 -O
-O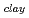
 3.0
3.0  -O
-O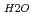 = ca. 2.8 AA ). These results suggested that interaction between water molecule and siloxane surface weaker than that between water molecules, although they were forced to be oriented.
= ca. 2.8 AA ). These results suggested that interaction between water molecule and siloxane surface weaker than that between water molecules, although they were forced to be oriented.
Minezaki, Yoshiaki; *; Niimura, Nobuo
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 60(8-9), p.1387 - 1391, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Saito, Kenichi*; Ichinose, Yuji; Kawanishi, Shunichi; Fukumura, H.*
Chemical Physics Letters, 291(3-4), p.433 - 437, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:36.14(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Niimura, Nobuo*
Tampakushitsu Kakusan Koso, 39(7), p.1283 - 1288, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Yonetani, Yoshiteru
no journal, ,
Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen exists not only on the Earth's surface as liquid water but also incorporated into minerals in the deep mantle as hydroxyl ion. At ambient pressure on the surface of the Earth, hydrogen in minerals generally takes an asymmetric position between two oxygen atoms, which forms a short covalent bond on the one side and a long and relatively weak hydrogen bond on the other side. However, it was theoretically predicted in 1970' that the hydrogen in ice locates at the center between two oxygen atoms under high pressure, which is so-called symmetrization of hydrogen bond. To investigate how the symmetrization affects on the physical properties of minerals, we conducted neutron diffraction experiments on  -AlOOH at high pressure. We observed that hydrogen reaches at the center between two oxygen atoms at 18.1 GPa. The present study revealed that even small change of hydrogen atomic position but the symmetrization can change the physical property of mineral.
-AlOOH at high pressure. We observed that hydrogen reaches at the center between two oxygen atoms at 18.1 GPa. The present study revealed that even small change of hydrogen atomic position but the symmetrization can change the physical property of mineral.